- Power: 16V ~ 32V DC (24V DC nominal)
- Communication: Standard Relay and Analog Outputs
- Conformity: ATEX, IECEx Certified (Zone 1, Zone2)
- IP65 Water and Dust Resistant
- Durable Aluminium Body
ATEX and IECEx Certified
Adjustable Alarm Level
Sensor-Adjust Technology
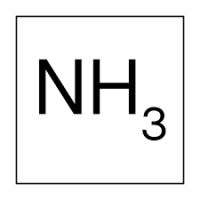
1- What is Ammonia?
Ammonia is a colorless, pungent, poisonous , corrosive and flammable gas with the chemical formula NH3 . It is also known as 'R717 refrigerant gas'. The liquid known as ammonia in the market is the dissolved form of this gas in water at certain rates, which is why ammonia gas is also called 'anhydrous ammonia'.
2- Where is Ammonia Found and Where is It Used?
Ammonia is an important industrial raw material and is one of the most produced inorganic substances in the world. Apart from its industrial production, it is found in very small amounts in living organisms because it plays a role in protein production.
Ammonia is used today mostly as a fertilizer in agriculture, as a raw material in the pharmaceutical industry, its aqueous solution as a cleaning agent in homes, in the fermentation industry to provide pH balance, as a refrigerant in the cooling industry, and in the mercerization process of cotton fabrics in the textile industry. Apart from these, it is an important substance used in metallurgy, plastics, petroleum, explosives and other industries.
3- Why is Ammonia Dangerous?
This toxic and flammable gas, used in many areas of industry, can pose a threat to personnel and facility safety if the necessary precautions are not taken.
Ammonia is 0.60 times less dense than air, so it rises when released into the air. However, in very humid environments, ammonia reacts with water vapor in the air, forming a fog denser than air and collecting near the ground. Ammonia accumulating in closed or poorly ventilated areas can be fatal. Since ammonia is a poisonous gas even in very small amounts, precautions should be taken in this regard first.
Toxicity
Ammonia is a poisonous gas for humans. When mixed with water, it is very toxic to aquatic organisms such as fish and amphibians, so it is considered a dangerous substance for the environment. According to the limits specified by the US National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, the long-term (10-hour) exposure limit value in the workplace is 25 ppm , the short-term (15-minute) exposure limit value is 35 ppm , and the environment with 300 ppm ammonia should be left immediately.
Karf&Scoot GD2G Ammonia Detector ensures your personnel safety by measuring the amount of ammonia in a potentially hazardous environment quickly and precisely between 0 and 100 ppm thanks to its electrochemical sensor technology. (For other gases and measurement ranges, you can review our GD2G Electrochemical Detector page.)
Corrosiveness
Ammonia causes corrosion on metal surfaces. For this reason, equipment such as pipes and valves made of copper, zinc and their alloys cannot be used during the transportation or use of ammonia.
Flammability
Although ammonia is a flammable gas, it requires special conditions to create a fire-explosion hazard. The lower explosion limit (LEL) of ammonia is 15% and the upper explosion limit (UEL) is 28%. In other words, in order for ammonia to burn, there must be at least 15% ammonia in the air and this rate must not exceed 28%. Ammonia fires mostly occur at ammonia cylinders or pipe leak points. Such fires cannot be fought directly with water, dry or foam fire extinguishing solutions are required.
4-How to Detect Ammonia?
Karf&Scoot GD2G Ammonia Detector Features
Although ammonia is easily noticed by people in case of leakage due to its strong odor, the sense of smell is lost in a very short time due to the fatigue of the olfactory cells in the nose and the presence of ammonia becomes undetectable. The sense of smell is not sufficient and reliable for ammonia detection. In environments where ammonia gas may potentially be present, detection should be done using professional gas detectors .
Karf&Scoot GD2G Ammonia Detector detects ammonia gas sensitively, quickly and reliably with its electrochemical sensor technology. It can be used alone or in harmony with the equipment in your facility thanks to its analog and digital signal outputs. It is suitable for use in explosive environments and has an Atex certificate. Its robust body made of stainless steel provides flawless measurement even in difficult industrial conditions. You can review our GD2G Electrochemical Detector page for other details.
Hazardous gas detection technologies are equipment of great importance for your personnel and facility safety. For more detailed information and our gas detection solutions specific to your facility, you can contact us from the contact addresses below or from our contact page.
Unauthorized copying and unauthorized quotation without citing the source is prohibited.
BG

1- Какво е амоняк?
Амонякът е безцветен, остър, отровен, корозивен и запалим газ с химична формула NH3 . Известен също като „хладилен газ R717“. Течността, известна на пазара като амоняк, е разтворената форма на този газ във вода в определени пропорции, така че амонячният газ се нарича още „безводен амоняк“.
2- Къде се намира амоняк? Къде се използва?
Тъй като амонякът е важна промишлена суровина, той е едно от най-често произвежданите неорганични вещества в света. Освен в промишленото производство, той се намира в много малки количества в живите организми, тъй като играе роля в производството на протеини.
Въпреки че днес амонякът се използва най-вече като тор в селското стопанство, той се използва като суровина във фармацевтичната промишленост, неговият воден разтвор като почистващ агент в домовете, във ферментационната промишленост за поддържане на рН баланс, като хладилен агент в охладителната промишленост и в процеса на мерсеризация на памучни тъкани в текстилната промишленост. Освен тях, това е важно вещество, използвано в металургията, пластмасата, петрола, експлозивите и други индустрии.
3- Защо амонякът е опасен?
Този отровен и запалим газ, използван в много области на индустрията, може да представлява заплаха за безопасността на персонала и съоръженията, ако не се вземат необходимите предпазни мерки.
Тъй като амонякът е 0,60 пъти по-малък от въздуха, той се издига, когато се освободи във въздуха. В много влажна среда обаче амонякът реагира с водните пари във въздуха и създава по-плътна мъгла от въздуха и се събира близо до земята. Амонякът, натрупан в затворени или лошо вентилирани среди, може да бъде фатален. Тъй като амонякът е отровен газ дори в много малки количества, първо трябва да се вземат предпазни мерки.
Токсичност
Амонякът е отровен газ за хората. Когато се смеси с вода, той е много токсичен за водни организми като риби и земноводни, така че се счита за опасно вещество за околната среда. Съгласно границите, определени от Националния институт по здраве и безопасност на труда на САЩ, граничната стойност на дългосрочна (10-часова) експозиция в работна среда е 25 ppm , краткосрочната (15 минути) гранична стойност на експозиция е 35 ppm , и средата, съдържаща 300 ppm
Детекторът за амоняк Karf&Scoot GD2G гарантира безопасността на вашия персонал чрез бързо и прецизно измерване на количеството амоняк в потенциално опасната среда в диапазона от 0 - 100 ppm, благодарение на своята електрохимична сензорна технология. (За други газове и диапазони на измерване можете да прегледате нашата страница за електрохимичен детектор GD2G .)
Корозивност
Амонякът причинява корозия на метални повърхности. Поради тази причина оборудване като тръби и вентили от мед, цинк и техните сплави не може да се използва по време на транспортирането или използването на амоняк.
Запалимост
Въпреки че амонякът е запалим газ, са необходими специални условия, за да представлява опасност от пожар и експлозия. Долната граница на експлозия (LEL) на амоняка е 15%, а горната граница на експлозия (UEL) е 28%. С други думи, за да изгори амоняк, трябва да има поне 15% амоняк във въздуха и в същото време тази скорост не трябва да надвишава 28%. Пожарите на амоняк възникват най-вече в местата на изтичане от тръби или тръби за амоняк. Такива пожари не могат да се гасят директно с вода; необходим е сух пожарогасителен разтвор или пяна.
4-Как да открием амоняк?
Характеристики на детектор за амоняк Karf&Scoot GD2G
Въпреки че амонякът се забелязва лесно от хората в случай на изтичане поради силната му миризма, обонянието се губи за много кратко време поради умората на обонятелните клетки в носа и наличието на амоняк става неоткриваемо. Обонянието не е достатъчно и надеждно за откриване на амоняк. Откриването трябва да се извършва с помощта на професионални газови детектори в среди, където потенциално може да присъства газ амоняк .
Karf&Scoot GD2G детектор за амоняк открива газ амоняк чувствително, бързо и надеждно с електрохимична сензорна технология. Благодарение на своите аналогови и цифрови сигнални изходи, той може да се използва самостоятелно или в хармония с оборудването във вашия обект. Подходящ е за използване във взривоопасни среди и има Atex сертификат. Неговият здрав корпус, изработен от неръждаема стомана, осигурява перфектно измерване дори при тежки индустриални условия. За други подробности можете да прегледате нашата страница за електрохимичен детектор GD2G .
Технологиите за откриване на опасни газове са оборудване от голямо значение за безопасността на вашия персонал и съоръжения. За по-подробна информация и решения за откриване на газ, специфични за вашето съоръжение, можете да се свържете с нас на адресите за контакт по-долу или чрез нашата страница за контакти .
Копирането без разрешение и цитирането без цитиране на източника е забранено.